Breakfast sausage is a beloved staple for many, adding a savory punch to mornings across the globe. However, a common ingredient in traditional breakfast sausage – nitrates – has raised concerns about its potential health effects. This article delves into the presence of nitrates in breakfast sausage, explores the associated health risks, and highlights alternative options for those seeking lower-nitrate choices.
We’ll examine how nitrates are used in sausage production, discuss the potential downsides of consuming high levels of nitrates, and explore various brands and methods that offer lower-nitrate alternatives. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions about your breakfast sausage choices and prioritize your well-being.
Nitrate in Breakfast Sausage
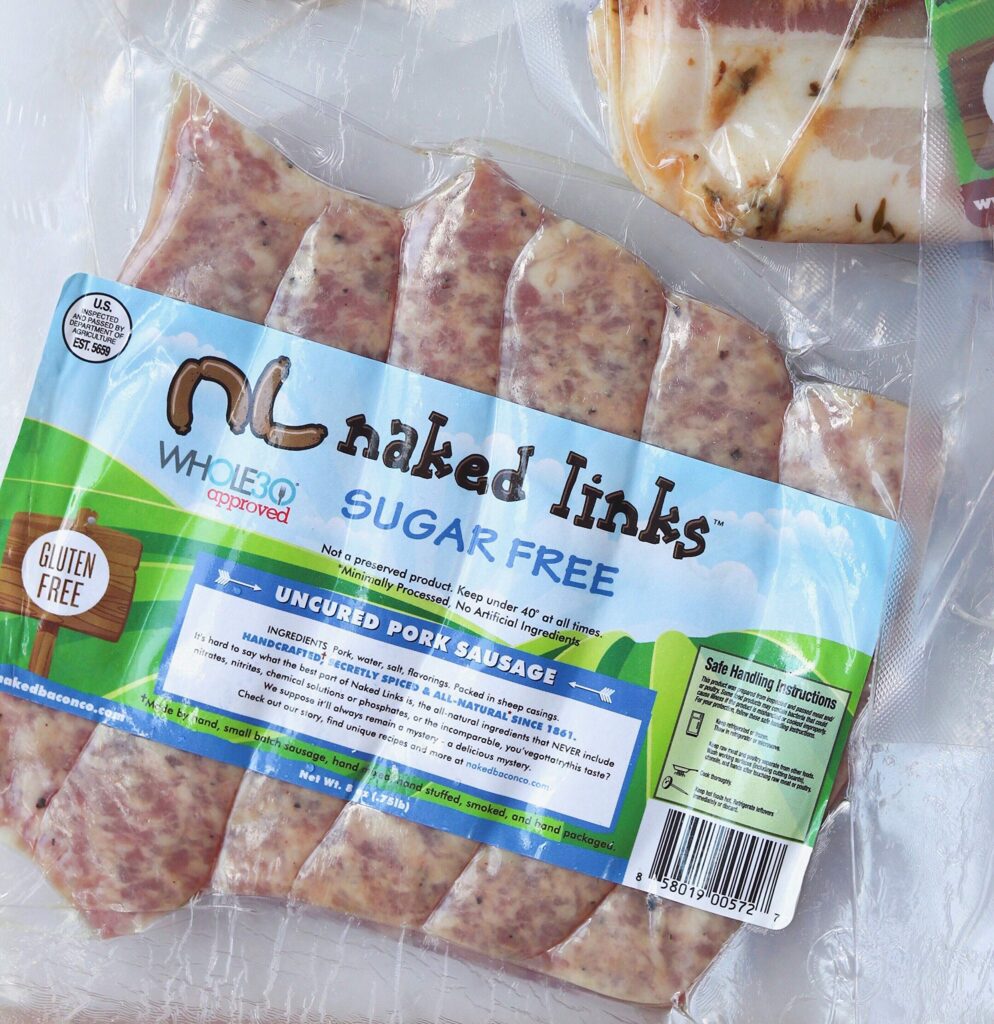
Nitrates are commonly added to processed meats like breakfast sausage as preservatives. They contribute to the characteristic pink color and enhance the savory flavor profile. The addition of nitrates helps inhibit bacterial growth, extending the shelf life of the product. While nitrates themselves aren’t inherently harmful, their conversion into nitrites within the body can raise concerns.
Nitrites are formed when nitrates react with stomach acid. These nitrites can then combine with amines in food to create nitrosamines, which are classified as potential carcinogens by the World Health Organization. The risk of nitrosamine formation is influenced by factors such as cooking temperature and time, as well as individual dietary habits.
Health Concerns of Nitrates

While moderate nitrate consumption from natural sources like vegetables is generally considered safe, excessive intake through processed meats has been linked to several health concerns.
One primary concern is the potential for increased risk of certain cancers, particularly colorectal cancer. Studies have shown a correlation between high processed meat consumption and an elevated risk of this disease. Nitrosamines formed in the body from nitrates are believed to play a role in this carcinogenic process.
Furthermore, nitrates can contribute to cardiovascular problems. They can interfere with blood flow by relaxing blood vessels excessively, potentially leading to hypertension. Additionally, nitrates may impact oxygen transport within the body, further exacerbating cardiovascular risks.
Lower-Nitrate Breakfast Sausage Options
Fortunately, for those seeking to reduce their nitrate intake, several lower-nitrate breakfast sausage options are available. Many brands now offer sausages made with alternative curing methods or natural preservatives that minimize the use of traditional nitrates.
When choosing lower-nitrate sausages, carefully read the ingredient list and look for terms like “uncured,” “no nitrates added,” or “naturally cured.” These labels indicate that the sausage has been processed without the addition of synthetic nitrates.
Alternative Curing Methods

Some manufacturers utilize alternative curing methods to enhance the flavor and preserve their breakfast sausages without relying on nitrates.
One such method is using celery powder as a natural source of nitrates. Celery contains naturally occurring nitrates, which are converted into nitrites during the curing process. This approach provides a lower-nitrate alternative compared to synthetic nitrate additions.
Another alternative involves employing smoking techniques to preserve and flavor the sausage. Smoking imparts antimicrobial properties and enhances the taste profile, reducing the need for added nitrates.
Natural Preservatives
Several natural preservatives can be used in place of traditional nitrates to extend the shelf life of breakfast sausages while minimizing potential health risks.
One common natural preservative is rosemary extract. Rosemary contains potent antioxidants that inhibit bacterial growth and contribute to the sausage’s flavor profile. Other natural preservatives include garlic powder, onion powder, and spices like paprika and black pepper, which possess antimicrobial properties.
Conclusion
While traditional breakfast sausages often contain nitrates for preservation and flavor enhancement, growing awareness of potential health concerns has led to a rise in lower-nitrate options. By understanding the role of nitrates in sausage production and exploring alternative curing methods and natural preservatives, consumers can make informed choices that align with their dietary preferences and health goals.
When selecting breakfast sausage, prioritize brands that utilize “uncured,” “no nitrates added,” or “naturally cured” labels. Embrace alternative curing methods like celery powder and smoking techniques, and opt for sausages incorporating natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, garlic powder, and spices. By making these conscious choices, you can enjoy a delicious and satisfying breakfast while minimizing your intake of potentially harmful nitrates.