Antarctica, the icy continent at the bottom of the world, holds a unique allure for scientists and adventurers alike. Its vast frozen landscapes, diverse wildlife, and crucial role in global climate regulation make it a subject of intense study and exploration. Among the nations with a strong interest in Antarctica is Argentina, which enjoys a geographical advantage that places it closer to this fascinating region than many others. This article delves into Argentina’s unique position relative to Antarctica, exploring its research endeavors, maritime border, and contributions to Antarctic science.
This article will examine Argentina’s geographic proximity to Antarctica, highlighting the distance between Tierra del Fuego and the icy continent. We will explore Argentina’s active role in Antarctic research and exploration, examining its scientific stations, research programs, and contributions to international collaborations. Furthermore, we will discuss the significance of Argentina’s maritime border with Antarctica and its implications for sovereignty claims and environmental protection.
Argentina’s Geographic Advantage
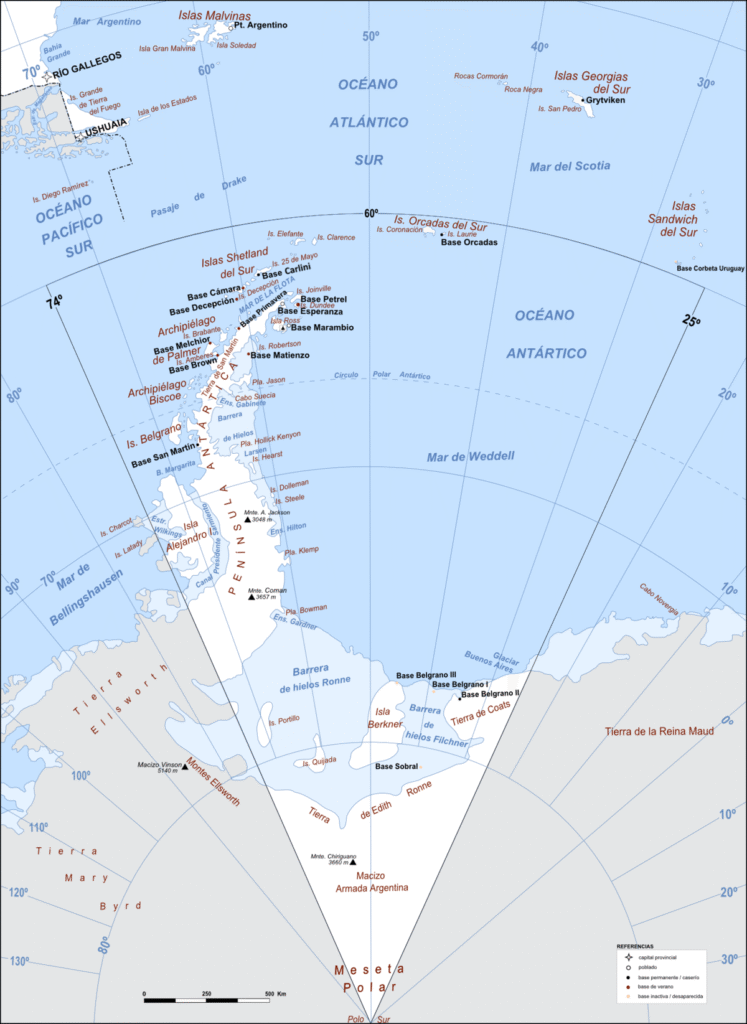
Argentina’s location in South America grants it a distinct advantage when it comes to accessing Antarctica. Situated at the southern tip of the continent, Argentina shares a maritime border with the icy realm, making it one of the closest countries to this remote region. This geographical proximity allows for easier and more frequent travel between Argentina and Antarctica, facilitating research expeditions, scientific collaborations, and logistical support.
The distance between Argentina’s southernmost point, Tierra del Fuego, and the Antarctic Peninsula is approximately 600 kilometers (372 miles). This relatively short distance compared to other nations with an interest in Antarctica significantly reduces travel time and costs, making it more feasible for Argentine researchers and explorers to conduct their work.
Antarctic Research & Exploration
Argentina has a long and distinguished history of involvement in Antarctic research and exploration. The country established its first scientific station on the continent in 1952, marking the beginning of its sustained commitment to understanding this unique environment. Today, Argentina operates several research stations across Antarctica, conducting diverse studies in fields such as glaciology, meteorology, marine biology, and geology.
Argentine researchers play a vital role in international collaborations within Antarctica. They actively participate in joint projects with scientists from other countries, sharing data, expertise, and resources to advance our understanding of the continent’s complex ecosystems and its impact on global climate change. These collaborative efforts highlight Argentina’s commitment to scientific cooperation and its recognition of the importance of international collaboration in addressing global challenges.
Argentine Scientific Stations
Argentina’s Antarctic research infrastructure includes several strategically located scientific stations, each equipped with specialized facilities for conducting various types of research. These stations serve as hubs for scientific activity, providing accommodation, laboratories, and logistical support for researchers working on the continent. Some notable Argentine Antarctic stations include:
- Base Marambio: Located on the Antarctic Peninsula, Base Marambio is Argentina’s largest and most important research station. It houses a wide range of facilities, including meteorological observatories, glaciological laboratories, and a helipad for transportation.
- Base Esperanza: Situated on the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, Base Esperanza focuses primarily on biological and geological research. Its location provides access to diverse ecosystems, allowing scientists to study the unique flora and fauna of the region.
Tierra del Fuego to Antarctica Distance
The distance between Argentina’s southernmost point, Tierra del Fuego, and Antarctica is approximately 600 kilometers (372 miles). This relatively short distance compared to other nations with an interest in Antarctica significantly reduces travel time and costs, making it more feasible for Argentine researchers and explorers to conduct their work.
This proximity allows for frequent maritime transport between Tierra del Fuego and the Antarctic Peninsula, facilitating the movement of personnel, equipment, and supplies. The shorter distance also enables faster response times for scientific missions and emergency situations, highlighting the practical advantages Argentina enjoys due to its geographical location.
Maritime Border with Antarctica
Argentina claims a significant portion of Antarctica based on its proximity and historical presence in the region. This claim is recognized by several international organizations, including the United Nations. The Argentine maritime border extends to the South Shetland Islands and the Antarctic Peninsula, encompassing a vast area of the continent’s coastline.
This maritime border grants Argentina exclusive rights to explore, exploit, and manage resources within its claimed territory. It also plays a crucial role in enforcing environmental protection measures and regulating activities within the region. Argentina actively participates in international agreements aimed at preserving Antarctica’s pristine environment and ensuring sustainable use of its resources.
Argentine Role in Antarctic Science
Argentina’s contributions to Antarctic science are significant and multifaceted. The country’s research stations, scientific programs, and international collaborations have made valuable advancements in understanding the continent’s climate, ecosystems, and geological history.
Argentine scientists play a leading role in monitoring climate change impacts on Antarctica, studying the melting of glaciers and ice shelves, and analyzing changes in sea levels. Their research provides crucial data for global climate models and informs policy decisions aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change.
Conclusion
Argentina’s unique geographical proximity to Antarctica has positioned it as a key player in Antarctic research and exploration. Its extensive scientific infrastructure, active research programs, and international collaborations have made significant contributions to our understanding of this fascinating continent.
From studying climate change impacts to exploring diverse ecosystems, Argentine scientists continue to push the boundaries of knowledge about Antarctica. As a nation with a strong commitment to environmental protection and international cooperation, Argentina plays a vital role in ensuring the sustainable future of this unique and fragile region.