Ice makers are a convenient appliance for keeping drinks chilled and enjoying refreshing treats. However, like any electrical device, they consume energy to function. Understanding how much electricity does an ice maker use is crucial for managing your household energy consumption and potentially saving money on your utility bills. This article will delve into the factors influencing ice maker energy usage, explore Energy Star certified options, and provide practical tips for minimizing your appliance’s energy footprint.
This comprehensive guide will first examine the average energy consumption of ice makers, followed by a detailed analysis of the factors that can significantly impact their electricity usage. We’ll then shed light on the benefits of choosing Energy Star certified models and offer actionable strategies to reduce your ice maker’s energy consumption.
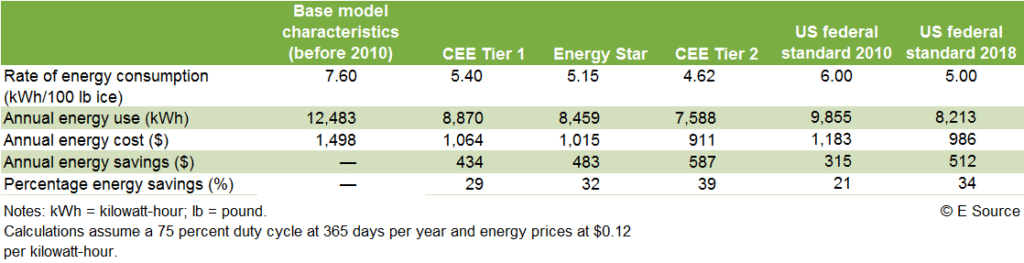
Ice Maker Energy Consumption
The amount of electricity an ice maker uses varies depending on its size, type, and operational frequency. Generally, a standard countertop or built-in ice maker consumes between 100 to 250 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year. This translates to approximately 0.3 to 0.7 kWh of energy used daily.
It’s important to note that these figures are estimates, and actual consumption can fluctuate based on individual usage patterns and the efficiency of the specific ice maker model. For instance, an ice maker producing larger cubes or operating more frequently will naturally consume more electricity compared to one making smaller cubes less often.
Factors Affecting Usage

Several factors contribute to the energy consumption of your ice maker:
Ice Production Frequency
The more frequently you use your ice maker, the higher its energy consumption will be. If you consistently produce large batches of ice daily, expect a significant increase in electricity usage compared to someone who only uses their ice maker occasionally.
Ice Cube Size
Larger ice cubes require more energy to freeze than smaller ones. This is because they have a greater volume of water that needs to be cooled and solidified. Opting for smaller ice cubes can potentially reduce your ice maker’s energy consumption.
Ambient Temperature
The temperature of the surrounding environment also plays a role in ice maker energy usage. In warmer climates, your ice maker will need to work harder to maintain the freezing temperatures required for ice production, leading to increased electricity consumption.
Ice Maker Type
Different types of ice makers have varying energy efficiency levels. Countertop models generally consume less energy than built-in units due to their smaller size and capacity. Additionally, some newer models incorporate advanced features like smart sensors and automatic shut-off functions that can help minimize energy waste.
Energy Star Certified Ice Makers
Choosing an Energy Star certified ice maker is a smart decision for both your wallet and the environment. These appliances meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Department of Energy (DOE).
Energy Star certified ice makers typically consume up to 10% less energy than standard models, resulting in significant savings on your electricity bills over time. They also often feature innovative technologies that further reduce energy consumption, such as improved insulation, efficient compressors, and smart controls.
Minimizing Energy Use

Beyond selecting an Energy Star certified model, you can implement several practical strategies to minimize the energy use of your ice maker:
Avoid Overfilling: Only fill the ice maker with the amount of water needed for your immediate requirements. Avoid overfilling as it forces the appliance to work harder and consume more energy.
Schedule Ice Production: If possible, schedule ice production during off-peak hours when electricity rates are typically lower. This can help you save money on your energy bill.
Clean Regularly: A clean ice maker operates more efficiently. Regularly remove any ice buildup or debris from the freezer compartment and the ice maker itself to ensure optimal performance.
Check for Leaks: Inspect your ice maker for any leaks, as water dripping can lead to increased energy consumption as the appliance works harder to maintain the freezing temperature.
Conclusion
Understanding how much electricity does an ice maker use is essential for making informed decisions about your appliance choices and energy consumption habits. By selecting an Energy Star certified model, adopting energy-saving practices, and being mindful of usage patterns, you can significantly reduce your ice maker’s environmental impact and potentially save money on your utility bills. Remember, even small changes can make a big difference in the long run.