In today’s world, electricity powers our homes and devices. Understanding how to safely use electrical power is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of your appliances. One key aspect of electrical safety involves choosing the right type of plug for your needs. This article will delve into the differences between polarized vs non-polarized plugs, exploring their functionalities, safety implications, and compatibility with various appliances.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of when to use each type of plug, empowering you to make informed decisions that prioritize both safety and optimal appliance performance.
Polarized vs Non-Polarized Plugs
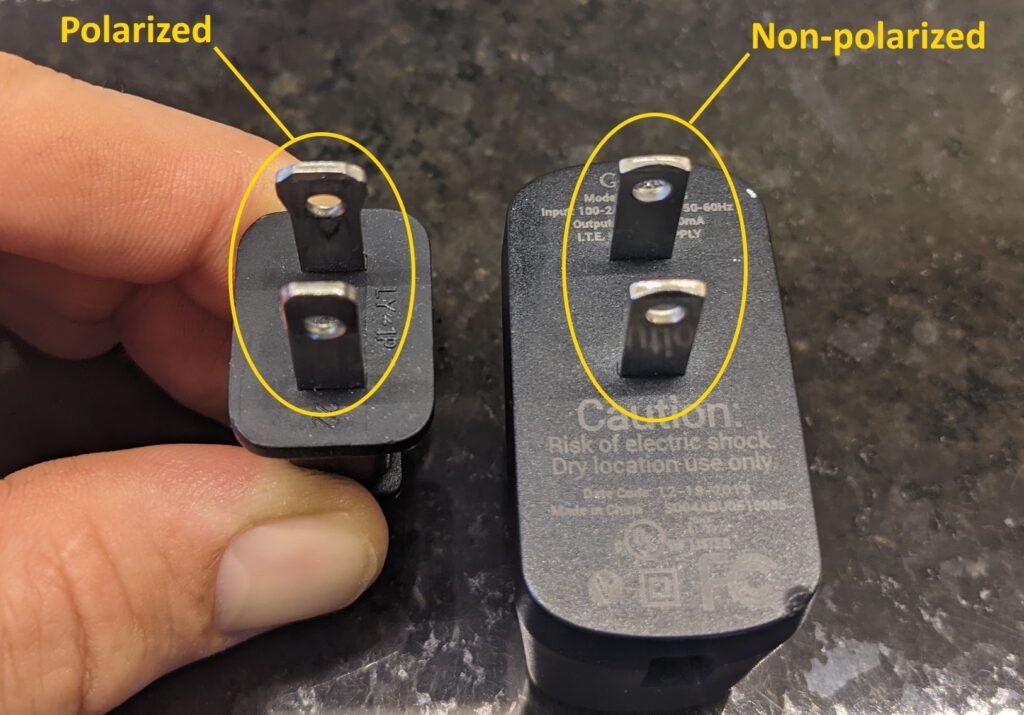
At their core, polarized plugs and non-polarized plugs differ in their prong configurations. A polarized plug features two prongs of distinct sizes: a wider “hot” prong and a narrower “neutral” prong. This design ensures that the hot wire, carrying the higher voltage, is always connected to the larger prong, while the neutral wire connects to the smaller one. Conversely, a non-polarized plug has two identical prongs, meaning there’s no distinction between the hot and neutral wires during connection.
This fundamental difference in design has significant implications for electrical safety and appliance functionality.
Electrical Shock Prevention

The primary advantage of a polarized plug vs non-polarized lies in its ability to prevent electrical shock. By mandating a specific connection for the hot and neutral wires, a polarized plug minimizes the risk of accidental contact with the live wire. If a fault occurs within an appliance, the hot wire is directed to the larger prong, preventing it from coming into contact with the user through the metal casing of the device.
Non-polarized plugs lack this safety feature, as they allow for any connection between the prongs and the wires. This increases the risk of electrical shock if a fault occurs, as the live wire could potentially be connected to the smaller prong, making it accessible to touch.
Appliance Compatibility
Appliance compatibility is another crucial factor to consider when choosing between polarized power cord vs non-polarized. Most modern appliances, particularly those with higher voltage requirements (like refrigerators, ovens, and computers), are designed to use polarized plugs. This ensures their safe and efficient operation by preventing electrical hazards and ensuring proper current flow.
Non-polarized plugs are generally suitable for low-voltage appliances like lamps, radios, and small electronics. However, it’s essential to consult the appliance’s manual to confirm its specific plug requirements. Using an incompatible plug can damage the appliance or pose a safety risk.
Safety Considerations

Prioritizing safety should always be paramount when dealing with electricity. Always inspect your plugs and cords for any signs of damage, such as fraying wires, loose connections, or cracks in the plastic casing. If you notice any issues, immediately discontinue use and replace the damaged cord or plug.
Furthermore, avoid overloading electrical outlets by plugging too many devices into a single socket. This can lead to overheating and potentially cause a fire hazard. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your appliances and adhere to local electrical codes for safe installation and usage.
Choosing the Right Plug
Selecting the appropriate plug type depends on several factors, including the appliance’s voltage requirements, intended use, and safety considerations.
For high-voltage appliances like refrigerators, ovens, or power tools, always opt for a polarized plug. This ensures proper current flow and minimizes the risk of electrical shock. For low-voltage appliances like lamps or radios, a non-polarized plug may suffice, but it’s crucial to consult the appliance’s manual for confirmation.
Remember, when in doubt, err on the side of caution and choose a polarized plug.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between polarized vs non-polarized plugs is essential for ensuring both the safety and efficient operation of your electrical devices. By choosing the right plug type based on appliance needs and adhering to safety guidelines, you can minimize the risk of electrical hazards and enjoy peace of mind knowing your home and appliances are protected.