The terms “roach” and “cockroach” often pop up in conversations about these unwanted houseguests, leaving many wondering if there’s a real difference between cockroach and roach. While both words refer to the same insect family, some subtle distinctions exist in how people use them. This article will delve into the nuances of these terms, exploring their origins, usage, and the fascinating world of cockroaches themselves.
This exploration will cover the scientific classification of cockroaches, examine the informal versus formal usage of “roach” and “cockroach,” and discuss their notorious reputation as household pests. We’ll also shed light on the remarkable resilience and adaptability that make these creatures such enduring survivors.
Cockroach vs Roach
The core question remains: what’s the difference between a roach and a cockroach? Essentially, there isn’t one. Both terms refer to insects belonging to the Blattodea order, characterized by their flattened bodies, long antennae, and six legs. They are often found in warm, humid environments and are known for their ability to reproduce rapidly.
While there is no official distinction between “roach” and “cockroach,” some people perceive a difference in formality. “Cockroach” is generally considered the more formal scientific term, while “roach” tends to be used in casual conversation or informal writing.
Regardless of the terminology, both words accurately describe these ubiquitous insects that can sometimes become unwelcome guests in our homes.
Blattodea Order

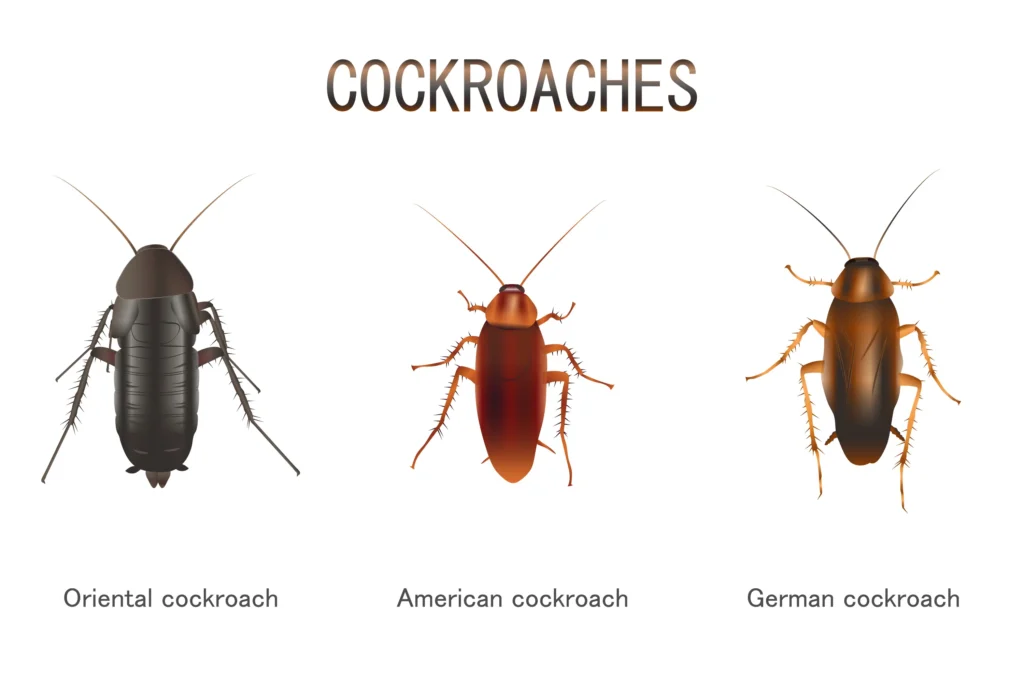
The Blattodea order encompasses a diverse group of over 4,600 species of cockroaches found worldwide. These insects exhibit a wide range of sizes, colors, and habitats. Some species are harmless and play beneficial roles in ecosystems by decomposing organic matter.
However, certain species, like the American cockroach and the German cockroach, have gained notoriety as common household pests. They are attracted to food sources, warmth, and moisture, often infesting kitchens, bathrooms, and basements.
The Blattodea order has a long evolutionary history, with fossil evidence suggesting their existence dating back over 300 million years.
Informal vs. Formal Terminology
As mentioned earlier, “roach” is often perceived as the more informal term, while “cockroach” carries a more formal connotation. This distinction can be influenced by regional dialects and personal preferences.
In casual conversations, people might say, “There’s a roach in my kitchen!” whereas in a scientific context, one would likely use the term “cockroach.” This difference in usage reflects the varying levels of formality associated with each word.
Household Pests

Cockroaches are notorious for their ability to infest homes and businesses, becoming unwelcome guests that can pose health risks. They contaminate food sources, spread allergens, and can trigger asthma attacks in sensitive individuals.
Their presence can also indicate unsanitary conditions, as they thrive in environments with poor sanitation practices. Controlling cockroach infestations requires a multi-pronged approach, including eliminating food sources, sealing entry points, and using appropriate insecticides.
Resilience and Adaptability
Cockroaches are renowned for their remarkable resilience and adaptability. They can survive extreme temperatures, limited oxygen levels, and even radiation exposure to a certain extent.
Their ability to thrive in diverse environments, from sewers to forests, is a testament to their evolutionary success. This resilience makes them challenging pests to control, as they can quickly adapt to changes in their surroundings.
Conclusion
While the terms “roach” and “cockroach” are often used interchangeably, subtle distinctions exist in their formality. Both words accurately describe the Blattodea order of insects, which includes both beneficial and harmful species.
Cockroaches have earned a reputation as household pests due to their ability to infest homes and spread allergens. However, their remarkable resilience and adaptability make them fascinating creatures that continue to thrive in various environments worldwide.