In today’s world, where fuel efficiency and environmental consciousness are paramount concerns, it’s crucial to adopt practices that minimize our impact. One often overlooked habit that contributes significantly to both fuel wastage and air pollution is idling your car. Leaving your engine running unnecessarily while stopped burns gasoline without providing any forward motion, a practice that can be easily avoided for substantial benefits. This article will delve into the reasons why you should stop idling your car, exploring its detrimental effects on fuel consumption, the environment, and your wallet. We’ll also discuss when idling might be necessary and offer practical alternatives to minimize this wasteful habit.
Idling Car Fuel Consumption
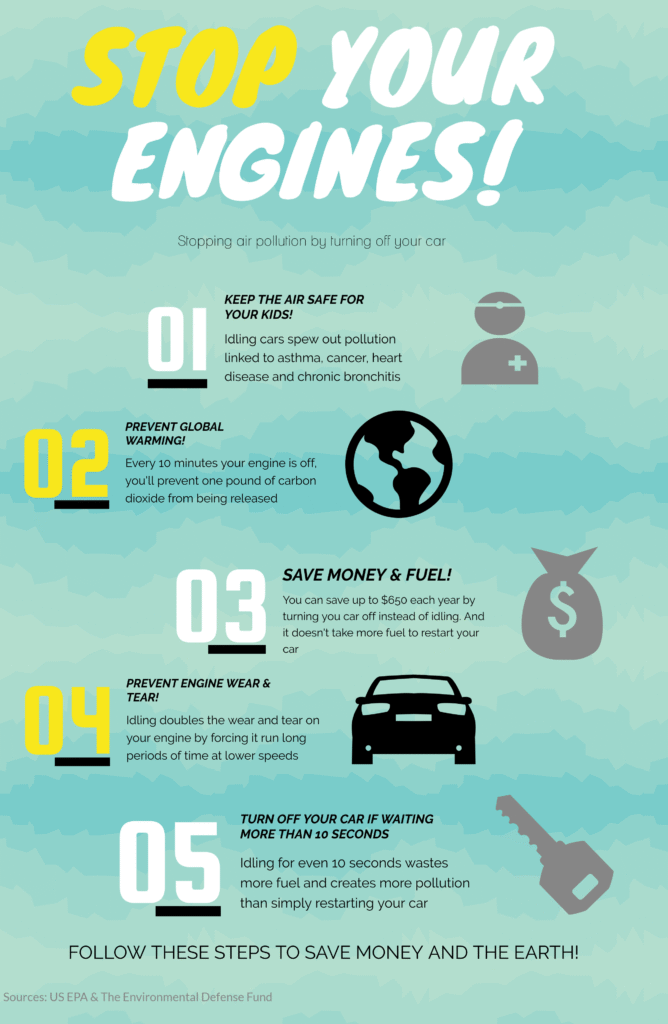
The amount of fuel consumed while idling may seem insignificant at first glance, but it adds up over time. A typical gasoline-powered car burns approximately 0.5 gallons of fuel per hour while idling. This means that if you leave your car running for just 10 minutes, you’re wasting a quarter of a gallon of gas – enough to drive several miles. Consider the cumulative effect of idling throughout the day or week, and it becomes clear that this seemingly harmless habit can significantly impact your fuel economy.
Furthermore, modern vehicles are designed with sophisticated engine management systems that optimize fuel consumption during operation. However, these systems are less efficient when the car is idling. The engine operates at a lower RPM, leading to incomplete combustion and increased fuel consumption. In essence, idling forces your engine to work inefficiently, burning more fuel than necessary for actual driving.
Environmental Impact of Idling
Beyond the financial implications, idling your car has a detrimental impact on the environment. Idling engines release harmful pollutants into the air, contributing to smog, respiratory problems, and climate change. These emissions include carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly in high concentrations. Nitrogen oxides contribute to acid rain and smog formation, while particulate matter can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing respiratory issues. VOCs are also harmful air pollutants that can react with other chemicals to form ground-level ozone, another major component of smog.
Benefits of Turning Off Your Engine
Turning off your engine when stopped for extended periods offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it significantly reduces fuel consumption, saving you money at the pump. Secondly, it minimizes your contribution to air pollution, creating a cleaner and healthier environment.
Furthermore, turning off your engine can also reduce wear and tear on your vehicle’s engine and other components. Idling puts unnecessary strain on the engine, leading to faster wear and tear. By shutting off the engine when stopped, you allow these components to rest, extending their lifespan and potentially reducing maintenance costs in the long run.
When to Idle Your Car
While it’s generally advisable to turn off your engine when stopped for extended periods, there are certain situations where idling may be necessary or even beneficial. For example, if you’re waiting in traffic for an extended period, keeping your engine running can help maintain a comfortable temperature inside the vehicle and power essential systems like the air conditioning.
Additionally, idling your car for a short period after driving in cold weather can allow the engine to warm up properly, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions during subsequent driving. However, it’s important to note that even in these situations, idling should be kept to a minimum.
Alternatives to Idling
Fortunately, there are several alternatives to idling your car that can help you save fuel, reduce emissions, and improve air quality. One option is to use the “start-stop” feature available in many modern vehicles. This technology automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle comes to a complete stop and restarts it when the driver releases the brake pedal.
Another alternative is to utilize public transportation, cycling, or walking whenever possible, especially for short trips. These modes of transportation produce zero emissions and promote a healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion
idling your car is an unnecessary habit that wastes fuel, pollutes the environment, and costs you money. By turning off your engine when stopped for extended periods, you can significantly reduce your environmental impact, save on fuel costs, and contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet. While there are certain situations where idling may be necessary, it’s important to minimize this practice and explore alternative options whenever possible. Embrace the benefits of turning off your engine and make a conscious effort to drive more efficiently and responsibly.