The question of whether it’s legal to keep a child out of school is a complex one that often sparks debate. While many parents prioritize their children’s education and understand the importance of attending school, there are situations where families may choose to homeschool or withdraw their children from traditional schooling. Navigating this issue requires careful consideration of legal requirements and potential consequences. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the laws surrounding compulsory education and the implications of keeping a child out of school.
This article will delve into the intricacies of compulsory education laws, explore the legal ramifications of school absence, examine jurisdiction-specific regulations, and discuss parental rights and responsibilities in this context. We will also highlight the importance of seeking legal counsel when facing complex educational decisions.
Compulsory Education Laws
Compulsory education laws are designed to ensure that children receive a basic level of education. These laws vary significantly from state to state and country to country, outlining the age range for mandatory schooling, attendance requirements, and exemptions. Generally, compulsory education mandates that parents or guardians send their children to school between certain ages, typically starting around 5 or 6 years old and continuing until a specific age, often 16 or 18.
The purpose of compulsory education is multifaceted. It aims to provide children with essential knowledge and skills, foster social development, and prepare them for future educational and career opportunities. By requiring attendance, governments seek to create a more educated and productive society. However, the specific details of compulsory education laws can be complex and subject to interpretation.
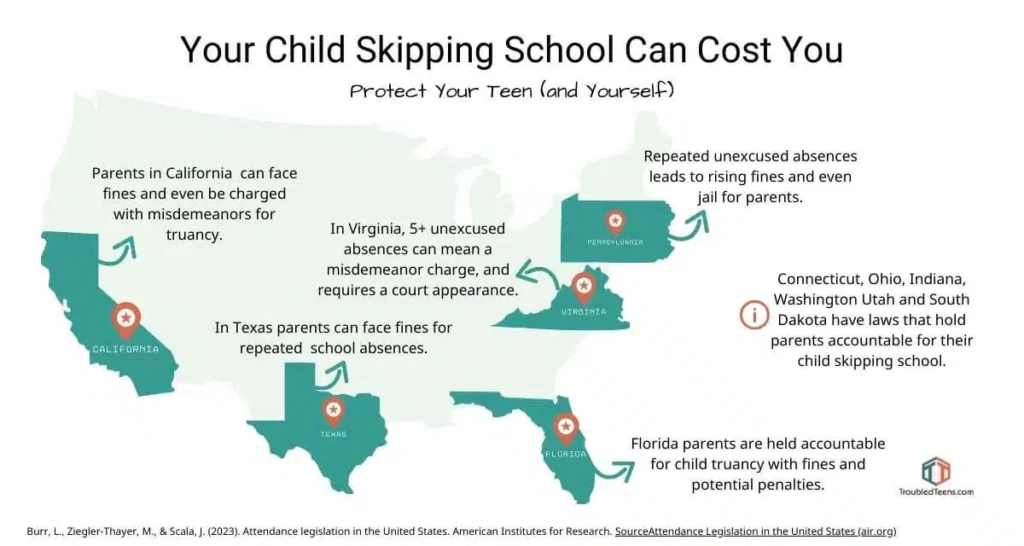
Legal Consequences of School Absence

Failure to comply with compulsory education laws can result in various legal consequences. These penalties may range from warnings and fines to more severe measures such as court orders or even imprisonment in some jurisdictions. The severity of the consequences typically depends on factors such as the child’s age, the duration of the absence, and the parent’s intent.
Parents who repeatedly fail to send their children to school may face escalating penalties. For example, a first offense might result in a warning or a small fine, while subsequent violations could lead to larger fines, community service, or even temporary loss of custody. In some cases, parents who deliberately withhold their children from education may be charged with criminal offenses.
Jurisdiction-Specific Regulations
It is crucial to understand that compulsory education laws and their enforcement vary significantly across jurisdictions. What is legal in one state or country may not be permissible in another. Therefore, it is essential for parents to research the specific regulations in their area and consult with local educational authorities or legal professionals for clarification.
For example, some states may have exemptions from compulsory education for religious reasons, homeschooling, or children with special needs. Others may have stricter attendance requirements or more lenient penalties for truancy. Understanding these nuances is vital to ensure compliance with the law.
Parental Rights and Responsibilities

Parents generally have a fundamental right to make decisions regarding their children’s upbringing, including educational choices. However, this right is not absolute and must be balanced against the state’s interest in ensuring that all children receive an education.
Parents have a responsibility to provide their children with access to schooling and to encourage their attendance. They should also be actively involved in their children’s education, monitoring their progress and communicating with teachers. While parents may have certain rights regarding educational choices, they must still comply with compulsory education laws and seek legal guidance when facing complex situations.
Seeking Legal Counsel
When navigating the complexities of compulsory education laws and potential legal consequences, it is highly recommended to seek legal counsel. An attorney specializing in education law can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances, jurisdiction, and legal options. They can help you understand your rights and responsibilities, explore alternative educational arrangements, and represent you in any legal proceedings.
Consulting with a lawyer early on can prevent misunderstandings, mitigate potential penalties, and ensure that you are making informed decisions regarding your child’s education.
Conclusion
Determining whether it is legal to keep a child out of school is a multifaceted issue that requires careful consideration of compulsory education laws, jurisdiction-specific regulations, parental rights, and potential legal consequences. While parents have certain rights regarding their children’s education, they must also comply with the law and seek legal guidance when facing complex situations. Understanding the intricacies of compulsory education and consulting with legal professionals can help ensure that families make informed decisions that are in the best interests of their children.