The sun’s rays are a powerful force, capable of both nourishing our bodies with vitamin D and potentially causing damage to our skin. Many people wonder if it’s still possible to get a tan after 4 PM, when the sun is lower in the sky. While UV radiation intensity does decrease as the day progresses, you can still experience tanning effects even later in the afternoon. This article will delve into the science behind UV rays and explore safe sun practices to help you enjoy the sunshine responsibly.
This comprehensive guide will cover the factors influencing UV intensity throughout the day, examine the possibility of tanning after 4 PM, and provide essential tips for protecting your skin from harmful sun exposure. By understanding these concepts, you can make informed decisions about sun safety and enjoy the benefits of sunlight while minimizing risks.
UV Rays & Sun Intensity
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. It comes in three main types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. While UVC rays are mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, UVA and UVB rays reach the surface and have significant impacts on our skin.
UVB rays are primarily responsible for sunburn and play a crucial role in tanning. They penetrate the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, causing DNA damage that triggers melanin production. Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin color and acts as a natural sunscreen by absorbing UV radiation.
The intensity of UV radiation varies throughout the day depending on several factors, including the time of day, latitude, altitude, and cloud cover. UV rays are strongest between 10 am and 4 pm when the sun is highest in the sky. During these peak hours, UVB radiation levels reach their maximum, increasing the risk of sunburn and tanning.
Tanning After 4 PM

While UV radiation intensity decreases after 4 PM, it doesn’t disappear entirely. You can still potentially get a tan later in the afternoon, but it will likely take longer than during peak hours. This is because the sun’s angle is lower, meaning the UV rays have to travel through more of the Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in reduced intensity.
The time it takes to tan after 4 PM depends on various factors, including your skin type, the amount of sun exposure, and individual sensitivity to UV radiation. People with fair skin will likely tan slower than those with darker skin tones due to their lower melanin content.
Remember that even if you don’t see a noticeable tan immediately, your skin is still being exposed to UV rays and accumulating damage. It’s crucial to practice sun safety habits consistently throughout the day, regardless of the time.
Sunscreen Protection
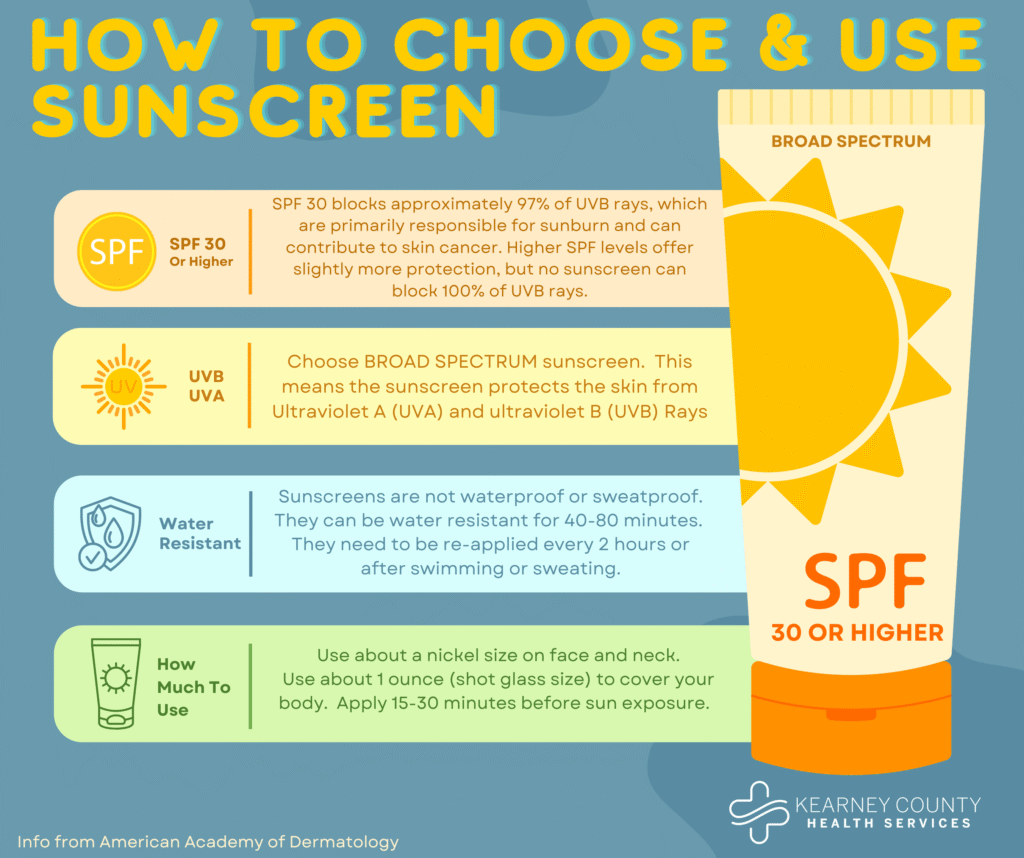
Sunscreen is an essential tool for protecting your skin from harmful UV radiation. It works by absorbing or reflecting UV rays, preventing them from penetrating your skin and causing damage. When choosing a sunscreen, look for one with an SPF (Sun Protection Factor) of 30 or higher.
SPF measures the amount of time it takes for UVB rays to redden your skin when using sunscreen compared to unprotected skin. For example, if you typically burn in 10 minutes without sunscreen, applying an SPF 30 sunscreen would theoretically allow you to stay in the sun for 300 minutes (10 x 30) before burning.
Apply sunscreen liberally and evenly to all exposed skin 15-20 minutes before going outside. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Shade & Sun Exposure

Seeking shade is another effective way to reduce your exposure to UV radiation. Trees, umbrellas, and buildings can provide natural shade during peak sun hours. When possible, try to limit your time in direct sunlight between 10 am and 4 pm.
Even on cloudy days, UV rays can penetrate clouds and reach your skin. Therefore, it’s important to wear sunscreen and seek shade even when the sky is overcast.
Safe Sun Habits
In addition to sunscreen and shade, there are several other safe sun habits you can adopt:
- Wear protective clothing: Opt for long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats to cover your skin. Choose fabrics with tight weaves that offer better UV protection.
- Sunglasses: Wear sunglasses that block 99% or more of UVA and UVB rays to protect your eyes from damage.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially when spending time outdoors. Dehydration can increase your risk of sunburn.
- Check your skin regularly: Examine your skin for any new or changing moles, freckles, or spots. Consult a dermatologist if you notice anything unusual.
Conclusion
While it’s possible to get a tan after 4 PM, UV radiation intensity decreases as the day progresses. Remember that even later in the afternoon, your skin is still exposed to harmful rays. By practicing safe sun habits, including wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, seeking shade during peak hours, and limiting sun exposure, you can enjoy the benefits of sunlight while protecting your skin from damage.