Dental X-rays are an essential tool for dentists to diagnose and treat a wide range of oral health issues. These images provide valuable insights into the teeth, gums, and surrounding bone structures, allowing dentists to identify problems that may not be visible during a regular examination. While some individuals may have concerns about the potential risks associated with dental x ray radiation vs cell phone, it’s important to understand that the amount of radiation used in dental X-rays is very low and the benefits often outweigh the minimal risks.
This article will delve into the various aspects of dental X-rays, exploring their benefits, potential risks, safety measures, different types available, and the level of radiation exposure involved. By providing a comprehensive overview, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your oral health care.
Benefits of Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays offer numerous advantages for maintaining optimal oral health. They enable dentists to detect problems that are not readily apparent during a visual examination, leading to early diagnosis and treatment. Some key benefits include:
- Detecting Cavities: X-rays can reveal cavities between teeth or under existing fillings, allowing for timely intervention before they progress and cause pain or further damage.
- Identifying Infections: Dental X-rays can help identify abscesses, bone infections, and other inflammatory conditions that may not be visible externally. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevents complications.
- Assessing Bone Structure: X-rays provide valuable information about the density and structure of jawbone, which is crucial for diagnosing periodontal disease, evaluating impacted teeth, and planning dental implants.
- Monitoring Treatment Progress: Dental X-rays can track the effectiveness of orthodontic treatments, root canal procedures, and other interventions, ensuring proper healing and alignment.
Risks of Dental X-Rays

While dental X-rays are generally safe, it’s important to be aware of potential risks associated with radiation exposure. However, the amount of radiation used in dental X-rays is significantly lower than that from everyday sources like cell phone radiation.
The primary concern regarding dental x ray radiation vs cell phone is the potential for long-term effects, such as an increased risk of cancer. However, the risk associated with dental X-rays is extremely low, and the benefits often outweigh this minimal risk.
Dental X-Ray Safety
Dental professionals prioritize patient safety by implementing various measures to minimize radiation exposure during X-ray procedures:
- Lead Aprons: Patients are typically covered with a lead apron to shield sensitive organs from unnecessary radiation.
- Collimation: A lead diaphragm restricts the X-ray beam to the specific area being examined, reducing scatter radiation.
- Digital Sensors: Digital sensors capture images with significantly lower radiation doses compared to traditional film X-rays.
Types of Dental X-Rays

There are several types of dental X-rays, each designed to provide different views and information:
Intraoral X-Rays
These X-rays are taken inside the mouth using a sensor placed between the teeth. They capture detailed images of individual teeth, roots, and surrounding bone structures.
- Bitewing X-Rays: Capture images of upper and lower teeth in contact, ideal for detecting cavities between teeth.
- Periapical X-Rays: Focus on individual teeth and their surrounding bone, useful for diagnosing infections, abscesses, and impacted teeth.
Extraoral X-Rays
These X-rays are taken outside the mouth using a sensor positioned near the head. They provide wider views of the entire jaw or specific areas.
- Panoramic X-Rays: Capture a panoramic image of the entire mouth, including all teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. Useful for identifying impacted teeth, bone abnormalities, and TMJ disorders.
- Cephalometric X-Rays: Focus on facial bones and their relationship to each other, often used in orthodontics to assess jaw growth and alignment.
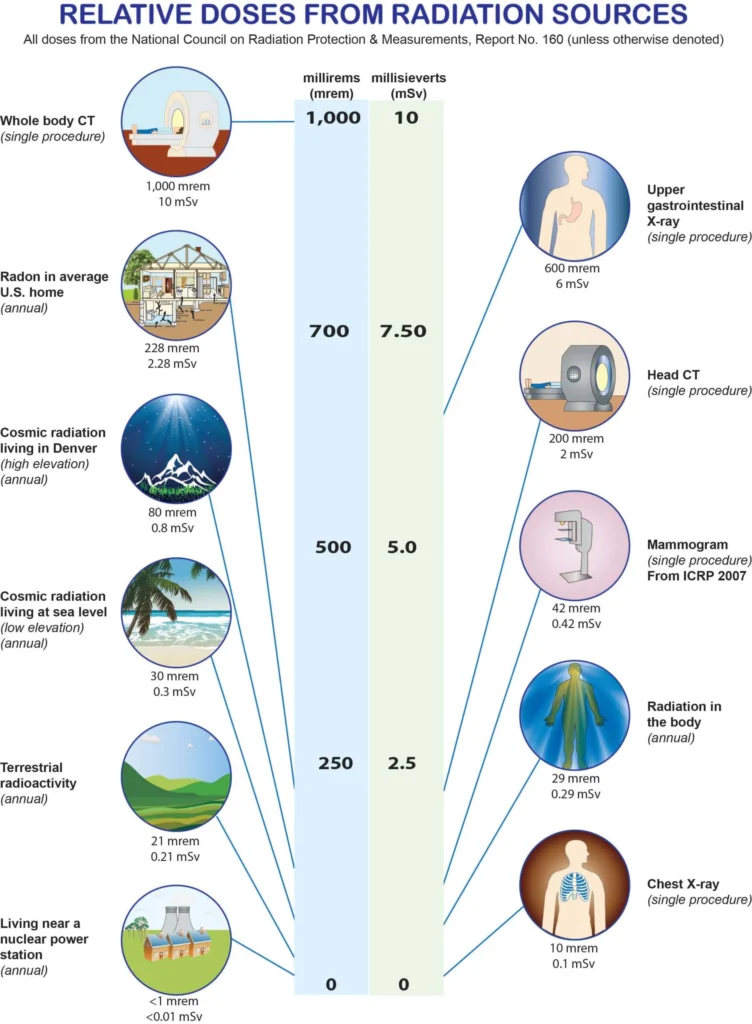
Radiation Exposure in Dental X-Rays
The amount of radiation exposure from dental X-rays is very low compared to other sources like medical imaging or natural background radiation.
Modern digital sensors significantly reduce radiation doses compared to traditional film X-rays. The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends that dental X-rays be taken as needed based on individual patient needs and risk factors.
Conclusion
Dental X-rays are a valuable tool for maintaining optimal oral health, enabling early detection and treatment of various dental problems. While there are potential risks associated with radiation exposure, the benefits of dental X-rays generally outweigh these minimal risks.
By adhering to safety protocols and utilizing modern digital technology, dentists can minimize radiation doses while providing patients with essential diagnostic information. Remember to discuss your concerns about dental x ray radiation vs cell phone with your dentist to make informed decisions about your oral health care.