In today’s world, where germs are constantly lurking around us, maintaining good hygiene practices is more important than ever. One of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect ourselves and others from illness is through proper hand hygiene. By diligently washing our hands with soap and water, we can significantly reduce the spread of harmful bacteria and viruses.
This article will delve into the importance of hand hygiene, exploring its numerous benefits and providing a comprehensive guide on how to wash your hands effectively. We’ll also examine the transmission of germs and bacteria and discuss practical strategies for preventing the spread of illness.
Importance of Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene plays a vital role in safeguarding our health and well-being. Our hands come into contact with countless surfaces throughout the day, picking up germs and bacteria along the way. These microorganisms can then be transferred to our eyes, nose, mouth, or even food, leading to infections and illnesses.
Proper hand washing breaks this cycle of transmission, effectively removing harmful pathogens from our hands. By adopting consistent hand hygiene practices, we create a barrier against infection and contribute to a healthier environment for ourselves and those around us.
Benefits of Hand Washing
The benefits of regular hand washing extend far beyond simply preventing illness.
Reduced Risk of Infections: Washing your hands with soap and water effectively eliminates a wide range of bacteria and viruses, significantly reducing the risk of contracting common infections such as colds, flu, and gastrointestinal illnesses.
Improved Overall Health: By minimizing exposure to harmful microorganisms, hand washing contributes to overall health and well-being. It helps strengthen our immune system and reduces the likelihood of developing chronic conditions associated with frequent infections.
- Enhanced Personal Hygiene: Hand washing is an essential component of personal hygiene, promoting cleanliness and contributing to a sense of well-being.
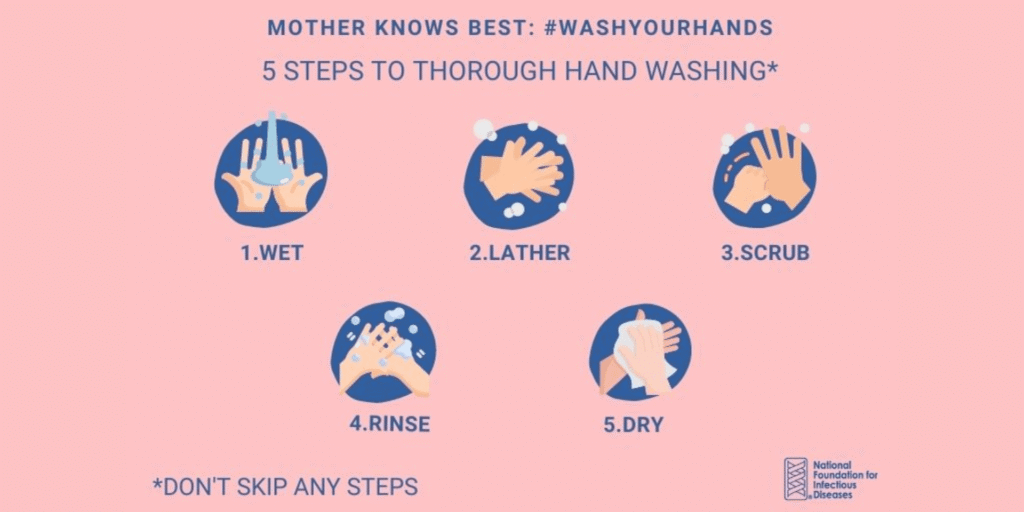
How to Wash Hands Properly
While hand washing may seem straightforward, there are specific steps to ensure thorough cleaning and effective germ removal.
Wet your hands: Begin by thoroughly wetting your hands with clean, running water (warm or cold).
Apply soap: Use enough soap to cover all surfaces of your hands, including palms, backs of hands, between fingers, and under nails.
Lather and rub: Create a rich lather by rubbing your hands together vigorously for at least 20 seconds. Be sure to scrub all areas mentioned above.
Rinse thoroughly: Rinse your hands well under clean, running water, ensuring that all soap residue is removed.
Dry completely: Dry your hands using a clean towel or air dryer.
When to Wash Your Hands
It’s important to wash your hands at specific times throughout the day to maximize their effectiveness:
- Before eating or preparing food: This helps prevent contamination of food with germs from your hands.
- After using the restroom: Always wash your hands after using the toilet to remove any harmful bacteria.
- After coughing, sneezing, or blowing your nose: These actions can spread germs, so hand washing is crucial afterward.
- After touching animals or their waste: Animals can carry various pathogens, so it’s important to wash your hands after contact.
- After handling garbage: Garbage often contains bacteria and other microorganisms that can be transferred to your hands.
Germs and Bacteria Transmission
Germs and bacteria are microscopic organisms that can cause a wide range of illnesses. They spread through various means, including:
- Direct Contact: Touching an infected person or their belongings.
- Indirect Contact: Touching surfaces contaminated with germs, such as doorknobs, countertops, or toys.
- Airborne Transmission: Inhaling droplets containing germs that are released when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Food and Water Contamination: Consuming food or water contaminated with bacteria or viruses.
Preventing Illness Spread
By practicing good hand hygiene and following other preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the spread of illness:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against preventable diseases is crucial for protecting yourself and others.
- Covering Coughs and Sneezes: Use a tissue or your elbow to cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Disinfecting Surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops.
- Staying Home When Sick: If you are feeling unwell, stay home to avoid spreading germs to others.
Conclusion
Hand hygiene is an essential practice for maintaining good health and preventing the spread of illness. By diligently washing our hands with soap and water, we create a barrier against harmful bacteria and viruses, protecting ourselves and those around us. Remember to wash your hands thoroughly at key moments throughout the day and follow other preventive measures to minimize the risk of infection.