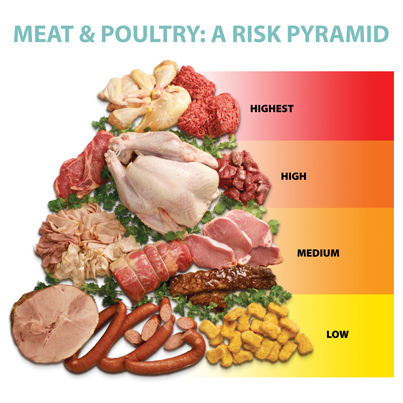
The world of meat offers a diverse range of flavors and culinary possibilities. However, it’s crucial to remember that raw meat can harbor harmful bacteria that pose a risk to our health. Determining the “dirtiest” meat is subjective and depends on various factors like processing methods and hygiene practices. While different types of meat can carry potential contaminants, ground beef often takes center stage in discussions about food safety due to its unique characteristics. This article delves into the concerns surrounding what is the dirtiest meat, focusing on ground beef and providing essential tips for safe handling and preparation to minimize the risk of foodborne illness.
This comprehensive guide will explore the specific risks associated with ground beef, shed light on common bacterial contaminants found in meat, and equip you with practical strategies to ensure your meat consumption remains a safe and enjoyable experience. From understanding proper storage techniques to mastering safe cooking practices, we’ll cover all the essential aspects of handling meat responsibly.
Dirtiest Meat: Ground Beef Concerns
Ground beef frequently earns the label of “dirtiest meat” due to its increased susceptibility to bacterial contamination during processing and preparation. This vulnerability stems from several factors:
- Comminution: The grinding process breaks down large chunks of meat into smaller particles, creating a larger surface area for bacteria to thrive.
- Mixing: Ground beef often involves blending different cuts of meat, potentially introducing bacteria from various sources.
- Handling: During handling and packaging, ground beef can come into contact with contaminated surfaces or equipment, increasing the risk of bacterial transfer.
These factors contribute to a higher likelihood of harmful bacteria being present in ground beef compared to other cuts of meat.
Bacterial Contamination in Meat

Various types of bacteria can contaminate meat, posing a significant threat to human health. Some common culprits include:
- Salmonella: This bacterium is responsible for salmonellosis, a foodborne illness characterized by diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. It’s commonly found in poultry, eggs, and raw meat products.
- E. coli: Certain strains of E. coli bacteria can cause severe food poisoning, leading to bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and even kidney failure. Ground beef is a common source of E. coli contamination.
- Campylobacter: This bacterium is another frequent culprit in foodborne illnesses, causing symptoms like diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps. It’s often found in raw poultry and unpasteurized milk.
These bacteria can survive at room temperature for extended periods, making proper handling and cooking crucial to prevent infection.
Food Safety Tips for Handling Meat
Adhering to strict food safety practices is paramount when handling meat to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination:
- Cleanliness: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling raw meat. Clean all surfaces, utensils, and cutting boards that come into contact with raw meat with hot soapy water or a sanitizing solution.
Separate: Keep raw meat separate from other foods in the refrigerator and during preparation to prevent cross-contamination. Use different cutting boards for raw meat and ready-to-eat foods.
Cook Thoroughly: Ensure meat is cooked to the recommended internal temperature to kill harmful bacteria. Use a food thermometer to verify doneness.
- Refrigerate Promptly: Refrigerate leftover meat within two hours of cooking or purchasing. Store it in airtight containers on a low shelf in the refrigerator to prevent dripping onto other foods.
Preventing Foodborne Illness

Foodborne illness can have severe consequences, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications. Taking proactive measures to prevent contamination is essential:
- Avoid Cross-Contamination: Be meticulous about separating raw meat from other foods during preparation and storage. Clean all surfaces and utensils thoroughly after handling raw meat.
- Wash Produce: Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly under running water before consumption, even if you plan to peel them.
- Cook Food Properly: Ensure all meat, poultry, and seafood are cooked to the recommended internal temperature. Use a food thermometer to verify doneness.
Safe Cooking Practices
Proper cooking techniques are crucial for eliminating harmful bacteria in meat:
- Use a Thermometer: A food thermometer is your best tool for ensuring meat is cooked to a safe internal temperature. Refer to reliable sources like the USDA for specific temperature guidelines based on the type of meat.
- Avoid Undercooking: Never undercook meat, as this can allow bacteria to survive and cause illness.
- Cook Thoroughly: Ensure all parts of the meat are cooked evenly. Use a fork or knife to check for doneness; the juices should run clear.
Conclusion
Understanding the potential risks associated with what is the dirtiest meat and implementing safe handling practices are essential for protecting your health. While ground beef often receives attention due to its vulnerability to contamination, all types of meat require careful handling and cooking to minimize the risk of foodborne illness. By adhering to the guidelines outlined in this article, you can enjoy a variety of delicious and safe meat dishes while safeguarding your well-being.