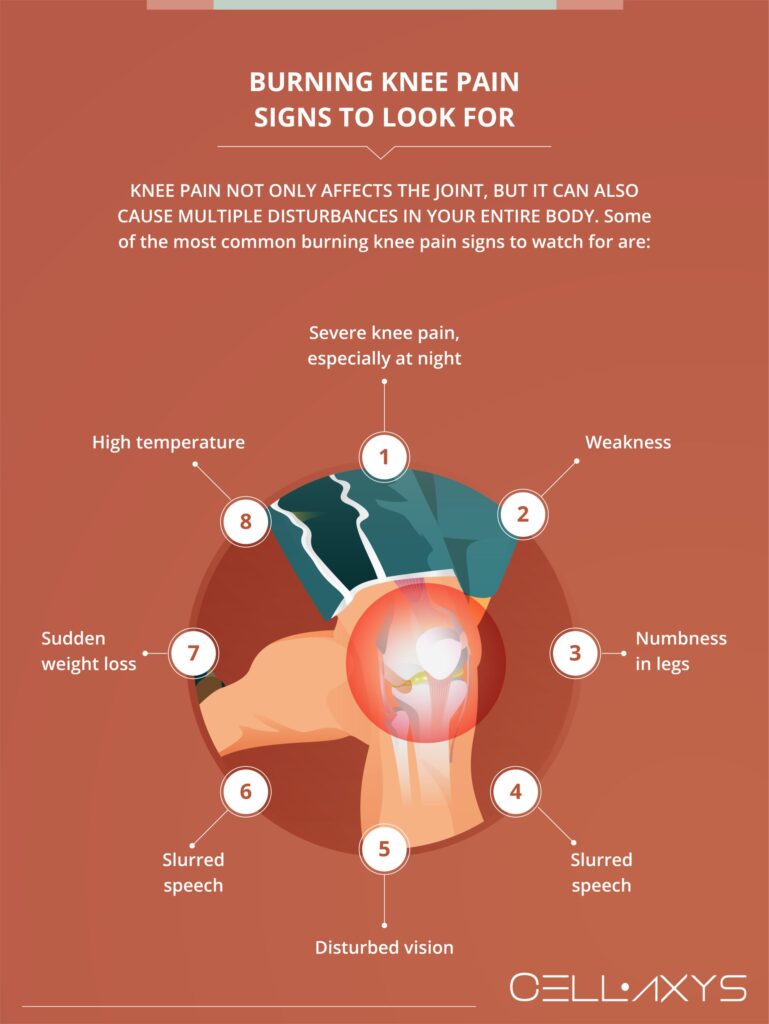
Joint pain is a common ailment that can significantly impact daily life. While some discomfort is normal, persistent or intense burning sensations in your joints can be alarming. This article delves into the various causes of why is my joint not burning properly and explores effective treatment options to alleviate this frustrating condition.
This comprehensive guide will examine potential triggers for joint burning pain, including inflammation, overuse injuries, and underlying medical conditions. We’ll also discuss various treatment strategies, ranging from medication and physical therapy to lifestyle modifications, empowering you to seek appropriate relief and improve your joint health.
Joint Burning Pain Causes
Joint burning pain can stem from a multitude of factors, often interconnected and requiring careful evaluation by a healthcare professional. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the most effective treatment plan.
Common Culprits
Several common culprits contribute to why is my joint not burning properly. These include:
- Inflammation: Inflammation within the joint tissues can lead to swelling, redness, and a characteristic burning sensation. This inflammation can be triggered by various factors, such as autoimmune diseases, infections, or injuries.
- Overuse Injuries: Repetitive motions or excessive stress on joints can result in overuse injuries like tendonitis or bursitis. These conditions often manifest as pain, stiffness, and a burning sensation, particularly after activity.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, gout, or fibromyalgia, can directly cause joint burning pain. Understanding the specific condition is essential for targeted treatment.
Inflammation and Joint Pain
Inflammation plays a significant role in many cases of joint burning pain. When tissues within the joint become inflamed, they release inflammatory chemicals that irritate nerve endings, leading to the characteristic burning sensation.
Triggers of Inflammation
Several factors can trigger inflammation in the joints:
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus cause the immune system to mistakenly attack healthy joint tissue, leading to chronic inflammation and pain.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections affecting the joints can also trigger inflammation and burning sensations.
- Injuries: Trauma to a joint, such as a sprain or fracture, can initiate an inflammatory response that contributes to pain and burning.
Overuse Injuries and Burning Sensation
Overuse injuries occur when joints are subjected to repetitive stress or strain beyond their capacity to recover. This can lead to inflammation and damage in the tendons, ligaments, and surrounding tissues, resulting in a burning sensation.
Common Overuse Injuries
Some common overuse injuries that cause joint burning include:
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of a tendon, often caused by repetitive motions, leading to pain and tenderness around the affected joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints, causing pain and stiffness.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist, often due to repetitive hand movements, resulting in burning, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers.
Medical Conditions Causing Joint Burning
Certain medical conditions can directly cause joint burning pain as a primary symptom.
Conditions to Consider
Some conditions that may contribute to why is my joint not burning properly include:
- Arthritis: A group of conditions characterized by inflammation and degeneration of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and burning sensations.
- Gout: A type of arthritis caused by uric acid crystal buildup in the joints, resulting in sudden, intense pain, redness, and swelling, often accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Fibromyalgia: A chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and other symptoms, including joint burning.
Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Treating joint burning pain effectively requires addressing the underlying cause.
Treatment Strategies
Various treatment options are available to alleviate joint burning:
- Medication: Over-the-counter or prescription medications can help manage pain, reduce inflammation, and address underlying medical conditions.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches prescribed by a physical therapist can strengthen muscles surrounding the affected joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making changes to your daily routine, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular low-impact exercise, and avoiding activities that aggravate your symptoms, can significantly impact joint health.
Conclusion
Joint burning pain can be a debilitating condition with various potential causes. Understanding the underlying factors contributing to your discomfort is crucial for effective treatment. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations is essential. By addressing the root cause and implementing appropriate strategies, you can alleviate joint burning pain, improve mobility, and enhance your overall quality of life.