Duct tape is a household staple known for its incredible adhesive power and ability to hold things together. But how much heat can this versatile material actually withstand? Understanding the melting point of duct tape is crucial for knowing its limitations and ensuring safe use in various situations. This article delves into the melting point of duct tape, explores its temperature limits, and examines its diverse applications while emphasizing safety precautions.
This article will first define the melting point of duct tape and explain how it’s determined. We’ll then discuss the specific temperature limits duct tape can handle before melting and explore the factors that influence these limits. Next, we’ll examine the wide range of uses for duct tape, highlighting its versatility in different applications. Finally, we’ll emphasize the importance of safety precautions when using duct tape in high-temperature environments.
Duct Tape Melting Point
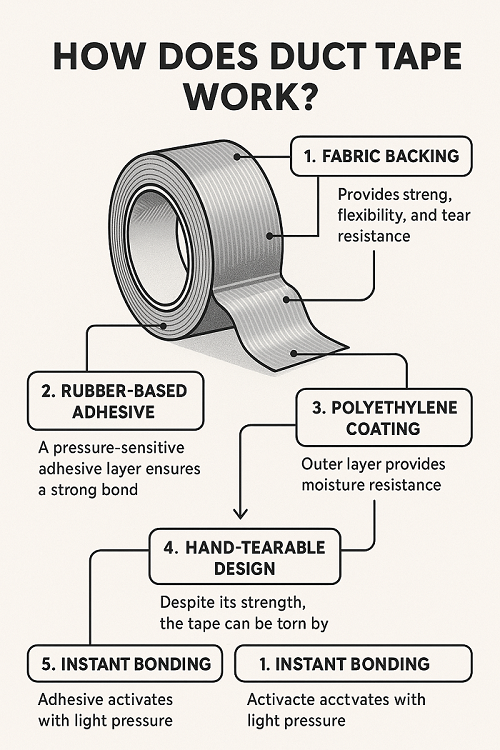
The melting point of duct tape refers to the temperature at which the adhesive and backing materials begin to soften and liquefy. This process is gradual, with the tape initially becoming pliable before eventually melting completely. The melting point of standard duct tape typically falls around 300°F (149°C).
Determining the melting point involves subjecting a sample of duct tape to controlled heating until it softens or melts. This process is often conducted in a laboratory setting using specialized equipment. The temperature at which the tape transitions from a solid to a liquid state is recorded as its melting point.
It’s important to note that the melting point can vary slightly depending on the specific composition and manufacturing process of the duct tape. Some specialty tapes designed for high-temperature applications may have higher melting points.
Temperature Limits
While duct tape possesses impressive heat resistance, it’s crucial to understand its limitations. Prolonged exposure to temperatures exceeding 300°F (149°C) will inevitably lead to can duct tape melt and compromise its structural integrity.
Several factors influence the temperature limits of duct tape:
- Material Composition: The type of adhesive and backing materials used in the duct tape directly impact its heat resistance. Some adhesives are more susceptible to softening or melting at lower temperatures than others.
Tape Thickness: Thicker tapes generally have a higher melting point due to the increased mass of material that needs to be heated.
Environmental Factors: Factors like humidity and airflow can affect how quickly duct tape heats up and reaches its melting point.
Uses of Duct Tape
Duct tape’s versatility extends across numerous applications, making it a valuable tool in various settings:
Repairing and Securing Items: Duct tape excels at mending tears, sealing gaps, and securing loose objects. Its strong adhesive bond can hold together items ranging from torn clothing to broken appliances.
Electrical Insulation: Duct tape’s ability to withstand moderate heat makes it suitable for insulating electrical wires and connections in temporary situations. However, it should not be used as a permanent insulation solution.
- Marking and Labeling: Duct tape’s bright colors and durability make it ideal for marking boxes, equipment, or areas requiring clear identification.
Safety Precautions
While duct tape is generally safe to use, certain precautions are essential, particularly when handling it in high-temperature environments:
- Avoid Prolonged Exposure to Heat: Never leave duct tape exposed to direct sunlight or heat sources exceeding its melting point for extended periods. This can lead to softening, weakening, and potential fire hazards.
Use Appropriate Ventilation: When working with duct tape in enclosed spaces, ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of fumes or vapors that may be released during heating.
Wear Protective Gear: When handling hot duct tape or working in environments where it’s exposed to high temperatures, wear appropriate protective gear, such as heat-resistant gloves and eye protection.
Applications in Different Environments
Duct tape’s adaptability allows it to function effectively in various environments:
Outdoor Use: Duct tape can withstand exposure to moisture, sunlight, and moderate temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for outdoor repairs and projects. However, prolonged exposure to extreme weather conditions may degrade its adhesive properties over time.
Industrial Settings: In industrial settings, duct tape is often used for sealing pipes, bundling wires, and marking equipment. Its durability and heat resistance make it a valuable tool in these demanding environments.
- Emergency Situations: Duct tape’s versatility and availability make it an essential item in emergency kits. It can be used to repair damaged shelters, secure belongings, or create makeshift bandages.
Conclusion
Duct tape is a remarkably versatile material with impressive adhesive properties and heat resistance. Understanding its melting point of around 300°F (149°C) and adhering to safety precautions when using it in high-temperature environments are crucial for ensuring its effectiveness and preventing potential hazards. From everyday repairs to industrial applications, duct tape’s adaptability continues to make it a valuable tool across diverse settings.