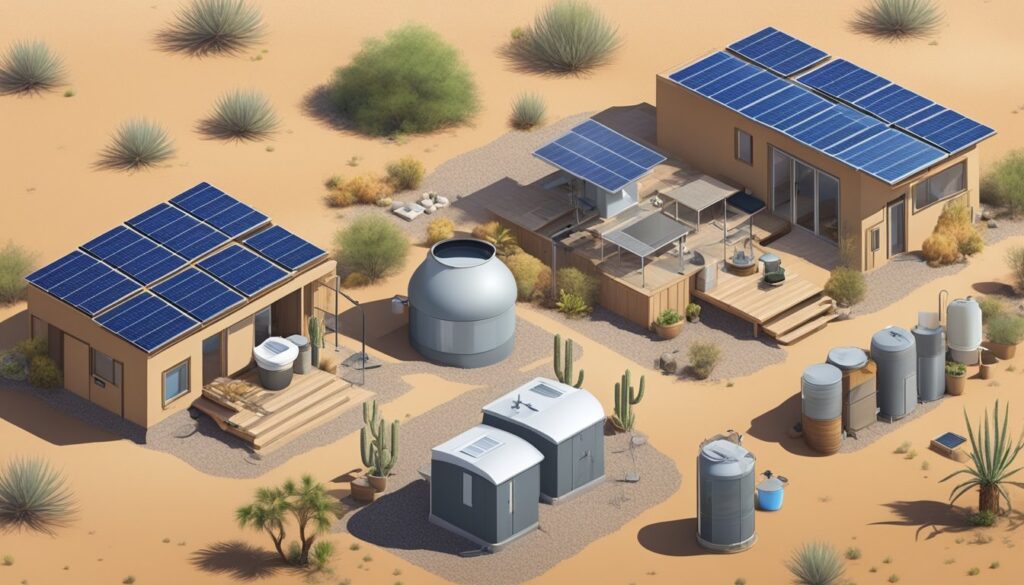
The allure of self-sufficiency and disconnecting from the traditional power grid is driving a growing number of people towards off-grid living. This lifestyle offers numerous benefits, including reduced utility bills, increased energy independence, and a closer connection to nature. However, before embarking on this journey, it’s crucial to understand the legal landscape surrounding can you live in a house without electricity.
This article will delve into the complexities of off-grid living, exploring the legal considerations, building codes, zoning regulations, and permits required to ensure compliance with local laws. By understanding these factors, aspiring off-gridders can make informed decisions and navigate the process smoothly.
Off-Grid Living Definition
Off-grid living refers to a lifestyle where individuals rely on self-generated resources for their energy, water, and waste management needs. This typically involves disconnecting from public utilities like electricity grids, municipal water systems, and sewage treatment plants. Instead, off-grid homes utilize alternative energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric generators to power appliances and lighting. Water is often sourced from wells or rainwater harvesting systems, while composting toilets or septic systems handle waste disposal.
The level of self-sufficiency varies among off-grid dwellers. Some may choose a partially off-grid approach, relying on the grid for certain necessities like internet access or backup power during emergencies. Others strive for complete energy independence, generating all their own power and managing their resources sustainably.
Legal Considerations for Off-Grid Homes

The legality of can you live in a house without electricity is primarily determined by local building codes and zoning regulations. These laws vary significantly across jurisdictions, so it’s essential to research the specific requirements in your area before making any decisions. Some areas may be more receptive to off-grid living than others, with progressive policies encouraging sustainable practices.
In some cases, local authorities may require homeowners to obtain permits or approvals for certain aspects of off-grid living, such as installing solar panels, drilling wells, or constructing septic systems. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even the forced removal of unauthorized structures.
Building Codes and Zoning Regulations
Building codes establish minimum standards for construction safety and habitability. These codes often address electrical wiring, plumbing, ventilation, and other essential aspects of a dwelling. When living off-grid, it’s crucial to ensure that your home meets these building codes, even if you are not connected to the public power grid.
Zoning regulations dictate how land can be used within a particular area. These regulations may specify permitted uses for residential properties, including restrictions on alternative energy systems or water sources. For example, some zoning ordinances may prohibit the installation of wind turbines in certain areas due to noise concerns or aesthetic impacts.
Alternative Energy Sources

Off-grid homes typically rely on renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric generators to meet their electricity needs. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, while wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind. Hydroelectric generators utilize the flow of water to produce power.
Each alternative energy source has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. It’s important to carefully consider your location, energy consumption patterns, and budget when selecting an appropriate system for your off-grid home.
Permits Required for Off-Grid Living
The specific permits required for off-grid living vary depending on the local jurisdiction and the nature of your project. Some common permits may include:
Building Permit
A building permit is typically required for any new construction or major renovations to an existing structure. This ensures that the work complies with local building codes and safety standards.
Electrical Permit
An electrical permit is often necessary when installing alternative energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines. This permits qualified electricians to inspect the installation and ensure it meets safety regulations.
Well Permit
If you plan to install a well for water supply, you will likely need a well permit from your local government agency. This ensures that the well is drilled properly and does not contaminate groundwater sources.
Septic System Permit
For off-grid homes without access to municipal sewer systems, a septic system permit may be required. This permits the installation of a septic tank and drain field to treat wastewater on-site.
Conclusion
Living off-grid can offer a rewarding and sustainable lifestyle, but it’s crucial to approach it with careful planning and legal awareness. Understanding the local building codes, zoning regulations, and permitting requirements is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential issues. By researching thoroughly and obtaining the necessary approvals, aspiring off-gridders can navigate the legal landscape successfully and enjoy the benefits of self-sufficient living.