The world of radio broadcasting offers a diverse range of programming, from news and talk shows to music and sports. But did you know that these broadcasts operate on different frequency bands? AM and PM radio refer to two distinct methods of transmitting audio signals, each with its own unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between AM vs PM radio can help you choose the best listening experience for your needs.
This article will delve into the intricacies of AM and PM radio, exploring their technical aspects, sound quality, and practical applications. We’ll compare their frequency bands, analyze their strengths and weaknesses, and guide you in selecting the right type of radio for your preferences.
AM Radio Explained
AM, or Amplitude Modulation, is a long-standing technology used for broadcasting audio signals. In AM transmission, the amplitude (strength) of the radio wave varies according to the audio signal being transmitted. This variation in amplitude carries the information, allowing listeners to receive the broadcast.
One key advantage of AM radio is its wide range. AM signals can travel long distances and penetrate obstacles like buildings and hills more effectively than PM signals. This makes AM ideal for broadcasting news and talk shows over large geographical areas.
However, AM’s susceptibility to interference is a significant drawback. Atmospheric conditions, electrical noise, and other electronic devices can disrupt the signal, leading to static and distortion. This often results in a less clear and crisp listening experience compared to PM radio.
AM Radio Applications
AM radio has traditionally been the primary platform for news, talk shows, and sports broadcasts. Its long-range capabilities make it suitable for reaching wide audiences, particularly in rural areas where signal reception can be challenging. Many local stations rely on AM frequencies to provide community-based programming and information.
PM Radio Explained

PM, or Phase Modulation, is a more modern technology that offers superior sound quality compared to AM. In PM transmission, the phase (timing) of the radio wave varies according to the audio signal. This subtle variation in phase carries the information with greater precision, resulting in a clearer and less distorted listening experience.
The advantages of PM radio extend beyond sound quality. PM signals are less susceptible to interference from atmospheric conditions and electronic devices. This ensures a more reliable and consistent listening experience, even in areas with high levels of electromagnetic noise.
PM Radio Applications
PM radio is widely used for broadcasting music, talk shows, and other programming that demands high-fidelity audio. Its superior sound quality makes it the preferred choice for listeners who appreciate clear and detailed sound reproduction. Many popular music stations operate on PM frequencies to deliver a rich and immersive listening experience.
Frequency Bands Comparison
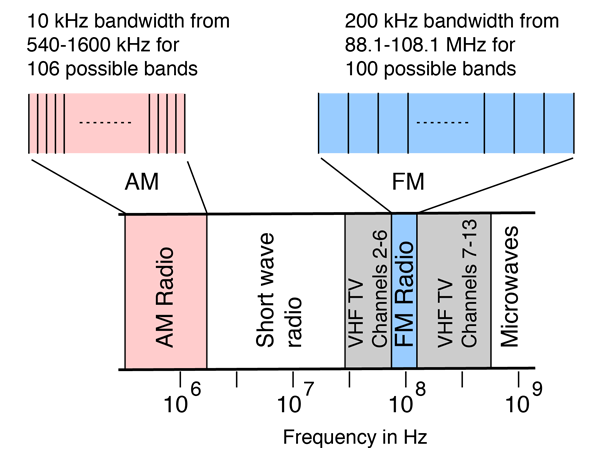
AM radio operates within a frequency range of 530 kHz to 1700 kHz, while PM radio utilizes frequencies between 88 MHz and 108 MHz. These distinct frequency bands allow for separate broadcasting channels and prevent interference between AM and PM stations.
The higher frequency range of PM radio enables it to transmit more information per second compared to AM. This allows for a wider bandwidth and the ability to broadcast higher-quality audio signals.
AM vs PM Sound Quality

PM radio generally offers superior sound quality compared to AM. The phase modulation technique used in PM transmission results in less distortion and a clearer, more detailed listening experience.
AM radio, on the other hand, is susceptible to interference and atmospheric noise, which can lead to static and distortion. This often results in a less clear and immersive listening experience.
Choosing the Right Radio Type
The best type of radio for you depends on your individual preferences and listening habits. If you prioritize sound quality and clarity, PM radio is the ideal choice.
For listeners who value long-range reception and access to local news and talk shows, AM radio may be a better option. Consider factors such as signal strength in your area, program availability, and personal listening preferences when making your decision.
Conclusion
AM and PM radio offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, catering to different listening needs. Understanding the technical differences between these frequency bands can empower you to make informed choices about your radio listening experience. Whether you seek crystal-clear audio or reliable long-range reception, there’s a perfect am vs pm radio solution waiting for you.