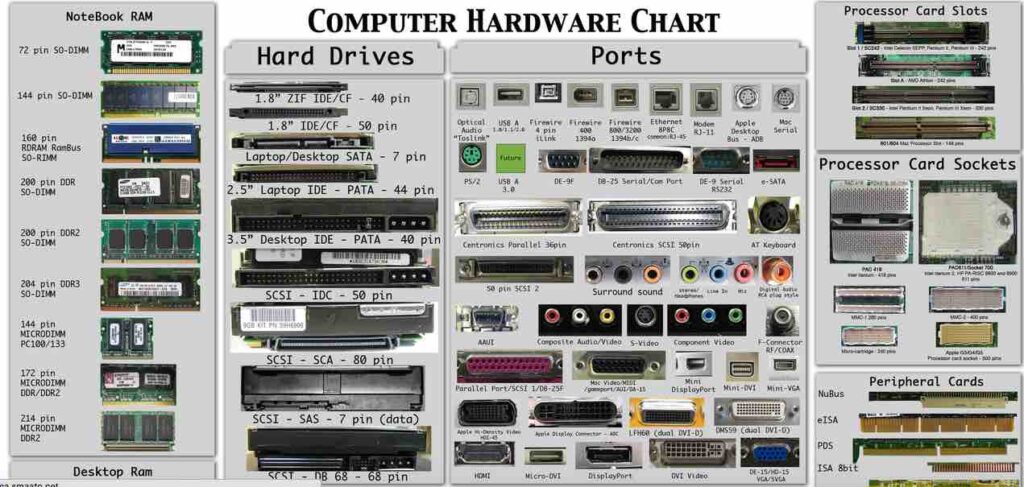
The world of vintage computing holds a unique charm, offering a glimpse into the evolution of technology. Whether you’re restoring a classic IBM or tinkering with a retro gaming rig, understanding the components within an old PC tower can be crucial for repairs, upgrades, or simply satisfying your curiosity. This guide will walk you through identifying common components of an old PC tower, from motherboards and CPUs to RAM and graphics cards.
This article is structured to provide a clear and concise overview of each component type. We’ll delve into their physical characteristics, identify key features, and offer tips for recognizing different generations and models. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of how to navigate the fascinating world of vintage PC hardware.
Identifying Old Motherboards
The motherboard is the central nervous system of any computer, connecting all the components of an old PC tower. Identifying it involves looking at its physical layout, chipset markings, and expansion slots.
Physical Characteristics
Older motherboards often feature a larger size compared to modern counterparts. They may have a beige or green color scheme and utilize ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) or PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) expansion slots. Look for the CPU socket, RAM slots, and various connectors for peripherals like keyboards, mice, and hard drives.
Chipset Markings
The chipset is a crucial component on the motherboard responsible for data transfer between different parts. Look for markings near the CPU socket or on the board itself. Common chipsets from older PCs include Intel 486, Pentium, AMD K5, and VIA Technologies offerings. These markings can help pinpoint the specific generation of the motherboard.
Expansion Slots
The type and number of expansion slots can provide clues about the motherboard’s capabilities. Older motherboards typically have ISA slots for legacy devices, followed by PCI slots for more modern peripherals. The presence or absence of AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slots indicates whether it supports older graphics cards.
Recognizing Vintage CPUs

The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the “brain” of the computer, executing instructions and performing calculations. Identifying vintage CPUs involves examining their physical appearance, model number, and socket type.
Physical Appearance
Older CPUs often have a larger size compared to modern counterparts. They may feature a square or rectangular shape with numerous pins on one side for connection to the motherboard. Look for markings indicating the manufacturer (Intel, AMD) and the specific CPU model.
Model Number
The model number is a crucial identifier for vintage CPUs. It typically consists of a series of letters and numbers that indicate the processor’s speed, architecture, and other specifications. Common examples include Intel Pentium II, AMD Athlon XP, and VIA C3 processors.
Socket Type
The socket type refers to the physical connector on the motherboard where the CPU is inserted. Older CPUs often used sockets like LGA 478, Socket A, or Socket 939. Identifying the socket type can help narrow down compatible CPUs for a specific motherboard.
Pinpointing RAM Types
RAM, or Random Access Memory, stores data that the CPU needs to access quickly. Identifying vintage RAM involves looking at its physical characteristics, module size, and speed rating.
Physical Characteristics
Older RAM modules often have a smaller size compared to modern counterparts. They may feature a single row of chips on one side and a notch for orientation. Look for markings indicating the manufacturer (Kingston, Corsair) and the specific RAM type.
Module Size
Vintage RAM modules typically came in sizes of 64MB, 128MB, or 256MB. The module size can be identified by looking at the markings on the module itself.
Speed Rating
The speed rating indicates how fast the RAM can access data. Older RAM modules often had speeds measured in MHz (megahertz). Common speed ratings for vintage PCs include DDR SDRAM at 266MHz, PC133, and PC100.
Spotting Graphics Cards from the Past

Graphics cards handle image processing and display output. Identifying vintage graphics cards involves examining their physical appearance, model number, and connector type.
Physical Appearance
Older graphics cards often had a larger size compared to modern counterparts. They may feature a single or dual-slot design with a fan for cooling. Look for markings indicating the manufacturer (Nvidia, ATI) and the specific graphics card model.
Model Number
The model number is a crucial identifier for vintage graphics cards. It typically consists of a series of letters and numbers that indicate the card’s capabilities, memory size, and other specifications. Common examples include Nvidia GeForce 256, ATI Radeon 9700 Pro, and Matrox G400.
Connector Type
The connector type refers to how the graphics card connects to the motherboard. Older PCs often used AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) connectors for graphics cards.
Conclusion
Identifying components of an old PC tower can be a rewarding journey into the history of computing. By understanding their physical characteristics, markings, and technical specifications, you can gain valuable insights into the evolution of technology and appreciate the ingenuity behind these vintage machines. Whether you’re restoring a classic system or simply exploring the past, this guide provides a foundation for navigating the fascinating world of old PC hardware.