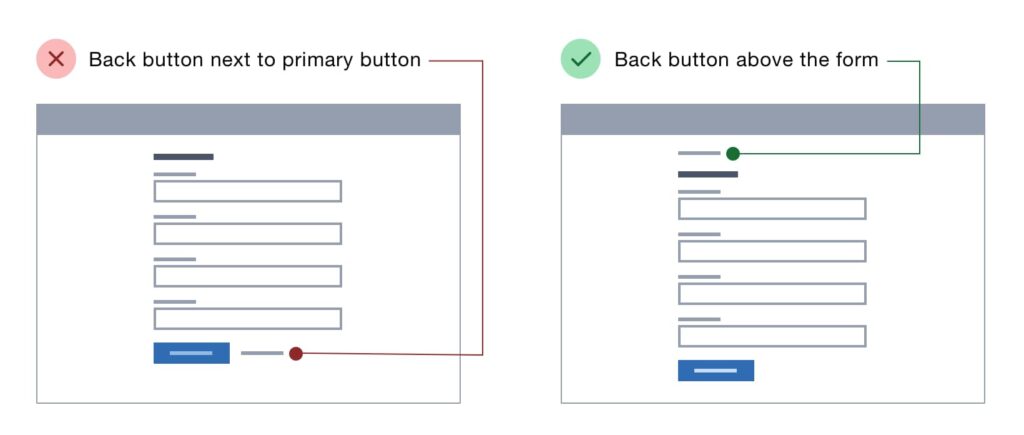
The internet is a vast and interconnected landscape, filled with countless websites offering diverse information and experiences. As users navigate this digital realm, they often find themselves exploring multiple pages within a single website or hopping between different sites altogether. This constant movement necessitates an efficient way to retrace steps and revisit previously viewed content. Enter the back button, a seemingly simple yet indispensable tool that empowers users to seamlessly traverse the web.
This article delves into the intricacies of the back button, exploring its functionality, its role in browser history, and its impact on user experience. We’ll examine how this ubiquitous button streamlines web page navigation, allowing users to effortlessly explore websites and retrieve desired information.
Back Button Functionality
At its core, the back button is a navigational element that utilizes the browser’s built-in history function. When clicked, it instructs the browser to revert to the previously visited webpage, effectively undoing the most recent forward action. This functionality relies on a record of every page a user has accessed during their browsing session, stored within the browser’s memory.
The back button operates independently of the website itself. It doesn’t require any specific code or implementation from the website developer; rather, it leverages the standard functionalities provided by the web browser. This universality ensures that users can consistently rely on the back button across different websites and platforms.
While the basic functionality remains consistent, there are subtle variations depending on the browser used. Some browsers may offer additional options, such as navigating to specific pages within the browsing history or clearing the entire history. However, the fundamental principle of returning to the previous page remains unchanged.
Browser History
The back button’s ability to navigate through previously visited pages hinges on the concept of browser history. Every website a user accesses is recorded in this chronological log, creating a trail of their online journey. This history serves as the foundation for the back button’s functionality, allowing users to retrace their steps and revisit desired content.
Browser history can be accessed directly through the browser interface, often by clicking on a dedicated “History” button or menu option. This allows users to view a list of all visited pages, organize them into folders, and even search for specific websites. The ability to manage and explore browsing history provides valuable insights into user behavior and preferences.
Web Page Navigation
The back button plays a crucial role in streamlining web page navigation, enabling users to efficiently explore websites and retrieve information. When navigating through multiple pages within a website, the back button allows users to quickly return to previous sections or review previously viewed content without having to manually type in URLs or search for links.
This seamless navigation enhances user experience by reducing frustration and saving time. Users can effortlessly delve into specific areas of interest, explore different sections of a website, and retrace their steps when needed, all with a single click. The back button empowers users to take control of their browsing journey and navigate websites with ease.
User Experience
The back button’s impact extends beyond mere functionality; it significantly influences user experience. Its intuitive design and consistent behavior across different browsers contribute to a sense of familiarity and control for users. Knowing that a single click can return them to the previous page fosters confidence and reduces anxiety associated with navigating complex websites.
Furthermore, the back button’s ability to streamline navigation enhances user satisfaction by allowing them to quickly access desired information and complete tasks efficiently. This seamless browsing experience contributes to a positive perception of the website and encourages users to explore further.
Benefits of Back Button
The benefits of the back button are multifaceted, impacting both users and website developers:
Enhanced User Experience: The back button simplifies navigation, reduces frustration, and empowers users to control their browsing journey. This leads to increased user satisfaction and a more enjoyable online experience.
Improved Website Accessibility: By enabling users to easily navigate between pages, the back button improves accessibility for individuals with disabilities who may struggle with complex website structures or require frequent revisits to specific information.
Increased User Engagement: The ease of navigation fostered by the back button encourages users to explore websites more thoroughly, leading to increased engagement and potentially longer browsing sessions.
Conclusion
The back button, though seemingly simple, is a fundamental element of web page navigation. Its ability to leverage browser history and seamlessly return users to previously visited pages significantly enhances user experience, streamlines website exploration, and contributes to overall online satisfaction. As the internet continues to evolve, the back button remains an indispensable tool for navigating the vast digital landscape.